Lupus Genetics – BANK1 Isoforms impact lupus pathogenesis differentially
Lead: Aalekhya Biswas
Team Members: Geethangili Madamanchi, Anto-Sam Crosslee
Collaborators: Vidya Ganesh, Julie Trinh, Chen Yanping, Rajalakshmy Ayilam Ramachandran
Project Summary:
Genetic studies have identified the B cell scaffold protein with ankyrin repeat 1 (BANK1) as a susceptibility locus for SLE and other autoimmune diseases. Clinical observations suggest that expression of the full-length BANK1 isoform (BANK1FL) is associated with lupus pathogenesis, whereas the exon 2–deleted isoform (BANK1Del) may confer protection. However, the mechanistic contribution of these isoforms to lupus development has not been established in vivo.
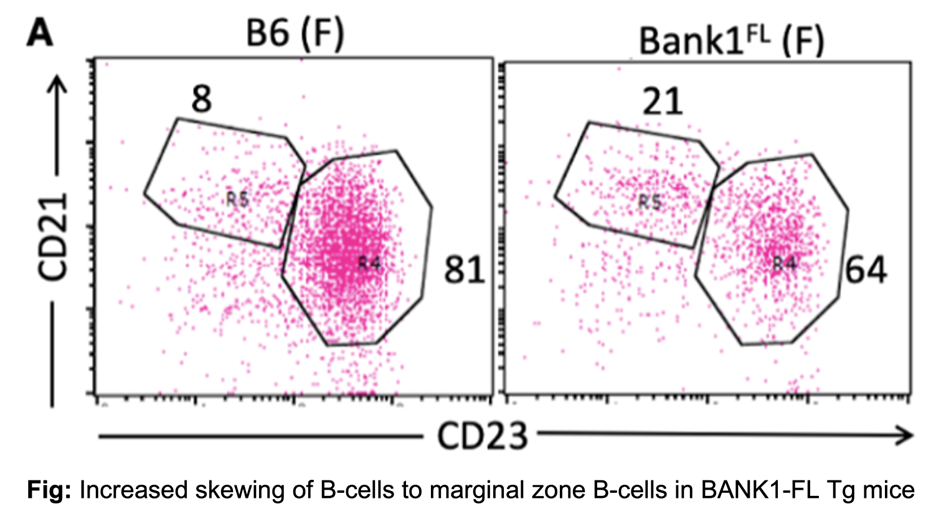
To address this knowledge gap, we generated two B cell–specific transgenic mouse models on a C57BL/6 background expressing either human BANK1FL or BANK1Del under the control of the CD19 promoter. BANK1FL transgenic mice displayed significant alterations in B cell differentiation, including expansion of marginal zone (MZ) and B1a B cells and a reduction in follicular (FO) B cells. These changes were accompanied by increased plasma cell differentiation, elevated serum total IgG and anti-dsDNA IgG levels, and modest renal pathology. Transcriptomic analyses revealed enhanced expression of class-switched IgG transcripts and activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID), a key regulator of class switch recombination. Notably, these autoimmune phenotypes were observed exclusively in female mice. In contrast, BANK1Del transgenic mice did not exhibit comparable immunological or pathological abnormalities, supporting a protective role for this isoform in lupus pathogenesis.
What is already known in the field?
- BANK1 is a critical adaptor protein involved in B cell receptor–mediated signaling. Genetic polymorphisms and alternative splicing of BANK1 are associated with increased risk of SLE and other autoimmune diseases.
- Clinical studies suggest opposing roles for BANK1 isoforms, with BANK1FL linked to disease susceptibility and BANK1Del associated with protection.
What is new?
- Development of B cell–specific transgenic mouse models expressing human BANK1 isoforms.
- First in vivo mechanistic evidence demonstrating that BANK1FL drives lupus-like immune dysregulation, while BANK1Del lacks pathogenic effects.
- Identification of sex-specific autoimmune phenotypes linked to BANK1FL
- Direct association of BANK1FL with enhanced class-switch recombination and autoantibody production.
Why is this important?
- B cell–targeted therapies are central to current lupus treatment strategies, yet patient responses remain variable. Understanding how specific BANK1 isoforms regulate B cell fate, autoantibody production, and disease susceptibility provides critical insight into lupus pathogenesis and heterogeneity.
- These findings highlight BANK1 isoform–specific signaling as a potential biomarker and therapeutic target, paving the way for more precise and personalized approaches to SLE treatment.
Ongoing/Future Steps
- Define the molecular signaling pathways downstream of BANK1FL and BANK1Del in B cells.
- Investigate the mechanisms underlying female-specific susceptibility in BANK1FL transgenic mice.
- Evaluate the interaction of BANK1 isoforms with established lupus-prone genetic backgrounds.
- Explore BANK1 isoform modulation as a potential therapeutic strategy in autoimmune disease.