Blocking Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase ameliorates inflammation in multiple target organs in rheumatic diseases
Lead: Yanping Chen
Team Members: Phuongthy Tran, Yong Du
Project Summary:
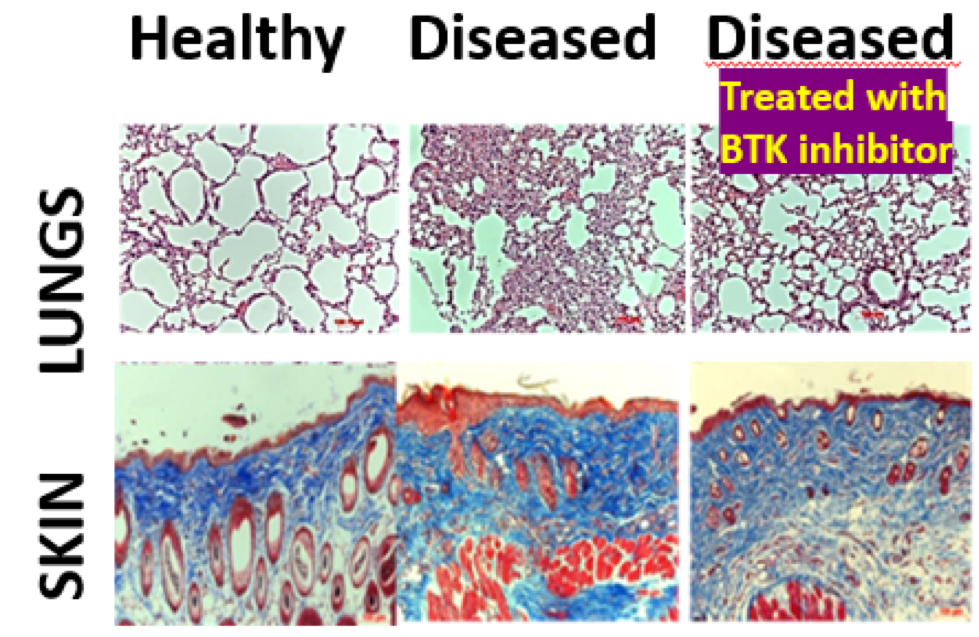
More than 50 million Americans are affected by various autoimmune diseases. Due to a lack of coordinated care, early diagnostic tests, and poor understanding of the underlying biology, autoimmune diseases are a public health crisis comparable to heart disease and cancer. Several studies have found that Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) is a key component of B cell receptor (BCR) signaling and functions as an important regulator of B cell development, differentiation and signaling. Recent studies also indicate its role in FcR-mediated myeloid cell signaling. Given the multiple roles of BTK in modulating leukocyte signaling, it is of potential interest as a therapeutic target in autoimmune diseases. We administered two BTK inhibitors to several mouse models to examine its effects on different autoimmune diseases in vivo. BTK inhibition reduced renal damage, renal dysfunction and improved renal pathology score in lupus nephritis mice. In an autoimmune disease model of systemic sclerosis (SSc), BTK inhibition reduced skin inflammatory cell infiltration andlung inflammation (see Figure). These finding indicate that BTK mediates inflammation in multiple target organs in autoimmune rheumatic diseases.
What is already known in the field?
- BTK is an important molecule for B-cell and myeloid cell activation.
- B cell depletion therapies are effective in anti-GBM disease, lupus and SSc
- BTK inhibition could ameliorate renal, skin, and brain disease in MRL/lpr mice.
- BTK is involved in inflammatory pathways.
What is new?
- BTK inhibition yields strong therapeutic efficacy against end organ damage in several autoimmune diseases, including SSc and renal disease.
Why is this important?
- Investigating the pathogenic mechanisms underlying autoimmune diseases can reveal novel therapeutic targets for other autoimmune diseases.
- Autoimmune diseases, like SLE, often involve inflammation in multiple organ systems.
- Since BTK inhibition ameliorates inflammation in multiple end organs, BTK inhibitors may be particularly effective in systemic autoimmune diseases where multiple end organs are targeted.
- Previous studies have already shown the safety of BTK inhibitors
Ongoing/future steps:
- Evaluate the therapeutic effects of BTK inhibition on disease development by administering varying doses of BTK inhibitor, to establish the optimal dose.
- To assess the degree to which B-cell alterations and myeloid cell alterations contribute to the efficacy of BTK inhibitors in systemic autoimmunity.